Discover the power of IDEA StatiCa Detail in handling complex structural design challenges. Whether it’s intricate frame joints, corbels, sections with openings, point loads, half joints, pier caps, diaphragms, or more, our article explores how IDEA StatiCa Detail simplifies even the most complex projects. Embrace advanced structural design with confidence.
As Structural engineers, who are fundamentally pragmatic, fact-oriented and rule-abiding, it is essential to begin with a foundational understanding. This includes recognizing that every reinforced and prestressed concrete structure must be systematically segmented into B-regions and D-regions as part of the design process. This theoretical approach is crucial for effective and efficient structural engineering
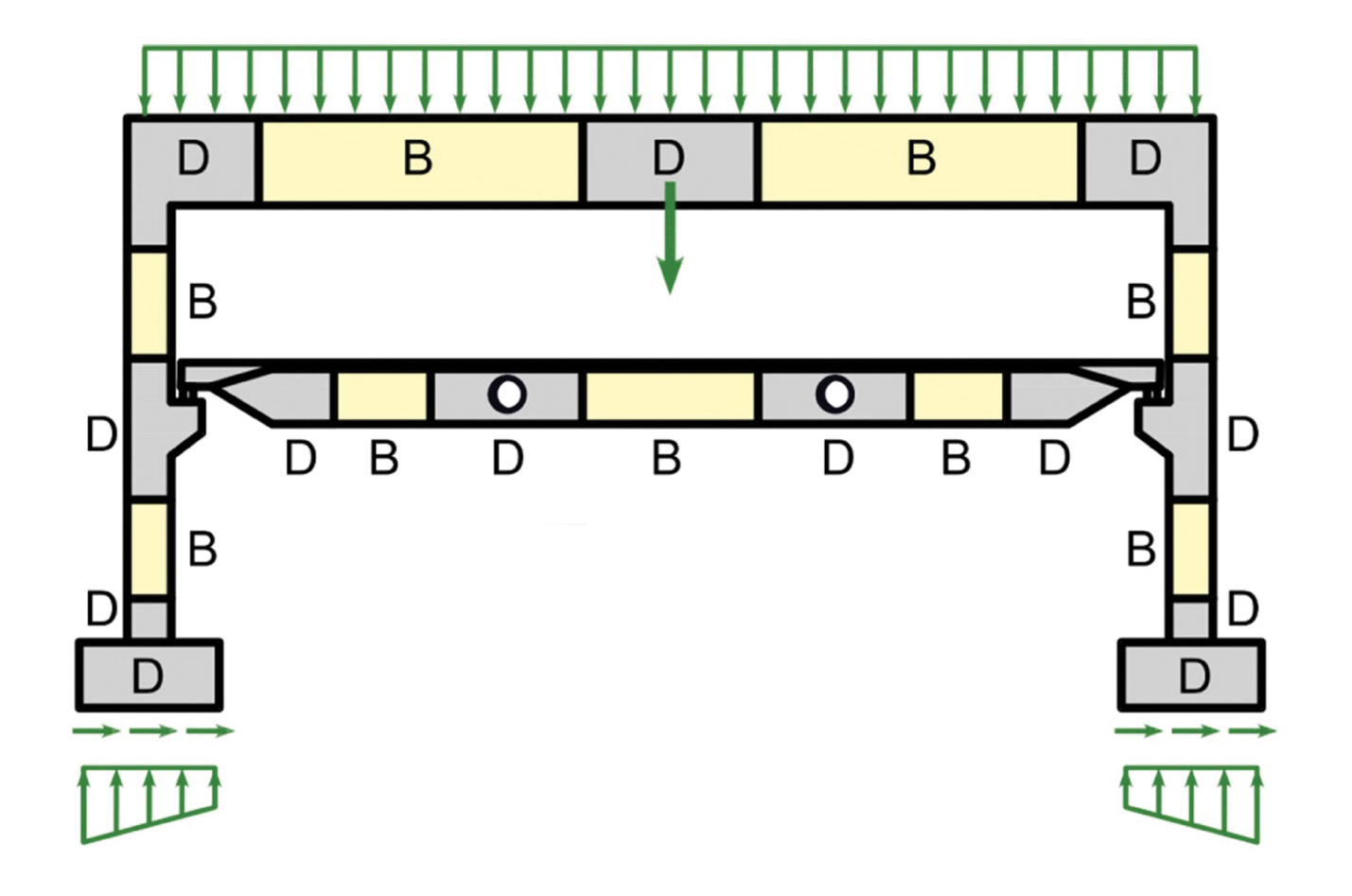
B-region, also known as Bernoulli regions, holds a fundamental aspect of classical beam theory – Bernoulli-Navier hypothesis of plain strain destruction. In these areas, applying the standard approach for analysis and verification is appropriate. These regions adhere closely to traditional structural engineering principles, allowing for more straightforward and conventional methods of assessment.
However, the D-regions, are also known as discontinuity or disturbed regions. In these parts, the previously mentioned hypotheses, which apply to B-regions do not apply to D-regions. Therefore, we must take sophisticated and advanced approaches to effectively analyse and design within complex and irregular sections of the structure.
Strut and Tie method (S&T)
A prominently used method that can be utilized in these scenarios is the equivalent truss method, also known as the Strut and Tie method (S&T) or the stress fields method. The fundamental assumption underpinning the Strut and Tie model is the negligible tensile strength of concrete. This approach simplifies the analysis by conceptualizing the behaviour of the D-region in the ultimate limit state as a basic truss. This method provides a more targeted and appropriate way to asses and design the more complex D-regions in concrete structures.
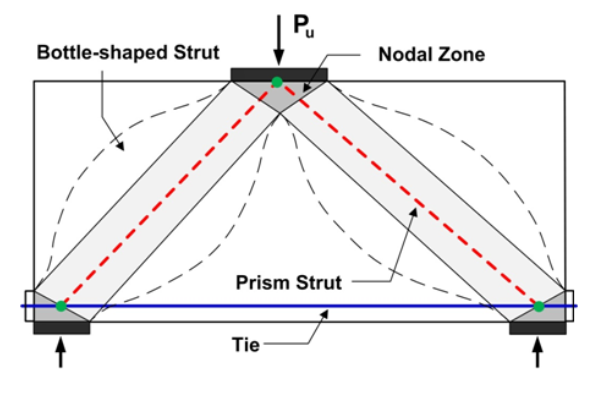
Ryan R. Setiadi, ST; Simplified pile caps design with Strut and Tie methods
While there are advantages, there are also notable disadvantages. These may include the potential for time-intensive processes, overly conservative or, conversely, risky designs due to inexperienced engineering. Establishing the appropriate truss model is challenging, and the iterative nature of the process can be exceedingly time-consuming. Often, under the pressure to deliver quick results, a structural engineer may focus solely on reinforcing the tensile tie, which can lead to significant errors. Additionally, the Strut and Tie method lacks guidance for evaluating serviceability limit states, such as deflection, stress limitation, and crack width check, all of which can significantly affect the service life of a structure.
This scenario may not be universal, but based on experience, it tends to be the case in the majority of situations. So, what’s the solution? What steps can you take to avoid wasting time and resources, or risking potential harm to your professional reputation?
Compatible Stress Field Method (CSFM)
The IDEA StatiCa Detail application operates on the principle of the Compatible Stress Field Method (CSFM), a distinctive approach for analyzing discontinuity regions, walls, and entire structural elements. This method expands upon existing stress field theories, offering a significantly automated alternative to traditional methods. Despite its straightforward nature, CSFM provides a highly accurate representation of how concrete structures respond to various loads. Additionally, it incorporates code checks for both ultimate and serviceability limit states.
This modern, non-linear analysis method focuses on 2D plane stress, adhering to fundamental and universally accepted code assumptions: that the tensile strength of concrete is negligible, and all tensile forces must be transferred through the reinforcement.
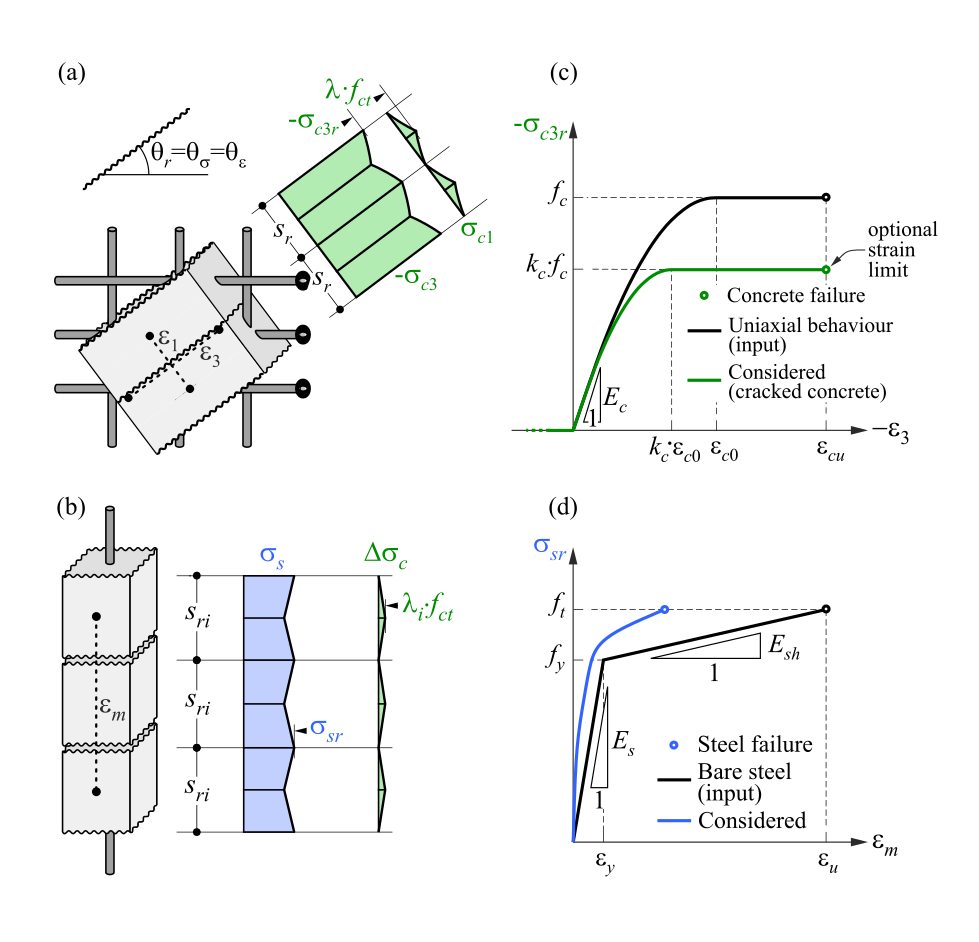
Are you intrigued to learn more about the method? Not a problem! Check out the article in the link below that explains more about how CSFM is utilised through the IDEA StatiCa Detail application.



